Feature-temporal predictions dynamically modulate performance, feature-based attentional capture, and motor response activity during visual search
Feature-temporal predictions dynamically modulate performance, feature-based attentional capture, and motor response activity during visual search
Williams, G. C.; Nobre, A. C.; Boettcher, S. E. P.
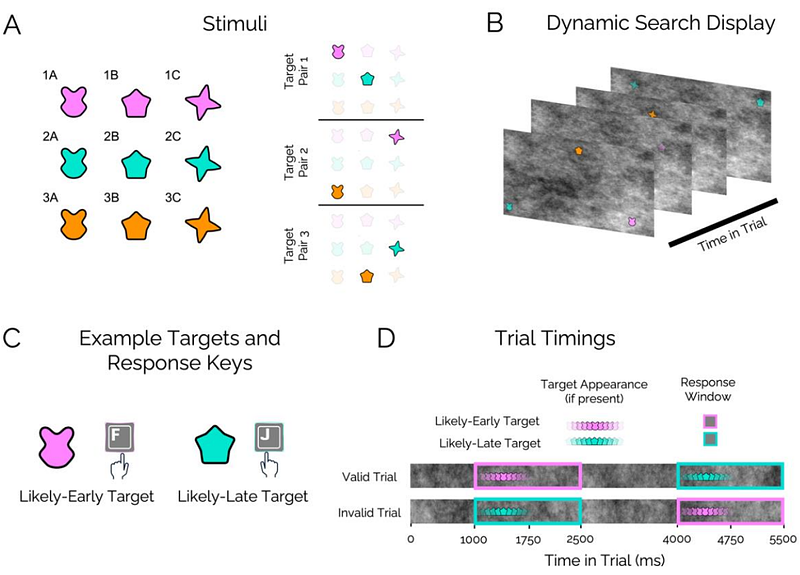
AbstractRecent research has investigated visual search in dynamic environments and considered how temporal predictions modulate behaviour over time. Spatiotemporal predictions have been shown to adaptively guide behaviour during search to improve target detection at temporally-likely locations. The utility of non-spatial, feature-temporal predictions is less intuitive. The present study investigated whether and how behaviour may be guided toward feature-temporally predictable targets during visual search in crowded and dynamic displays. We tested 1) whether visual attention is guided toward target-relevant features in a temporally specific manner and 2) whether our motor system is temporally tuned accordingly. Participants searched for two distinct targets (non-overlapping colour-shape combinations) in a free-viewing dynamic visual-search task. During an initial learning session, each target identity appeared at a predictable time. In a following testing session, some targets appeared at unpredicted times. Target locations were always unpredictable. We compared the efficiency of identifying targets appearing at predicted versus unpredicted times to test for performance benefits of feature-temporal predictability. In addition, we measured whether gaze fixation was captured by distractors that shared overlapping features with temporally predicted targets. Electromyography recordings were used to test for anticipatory muscle activity tuned to the timing of predictable targets. Results indicated that learning the task regularities led to dynamic modulation of participant efficiency at identifying targets, their feature-based attentional capture, and temporally tuned muscle activity. The work highlights the flexibility of temporal expectations in guiding behaviour even under spatial uncertainty.