Ionic liquid-coated lipid nanoparticles promote enhanced red blood cell hitchhiking
Ionic liquid-coated lipid nanoparticles promote enhanced red blood cell hitchhiking
Khare, P.; Edgecomb, S. X.; Hamadani, C. M.; Taylor, G. R.; Caprara, R.; Tanner, E. E. L.; Manickam, D. S.
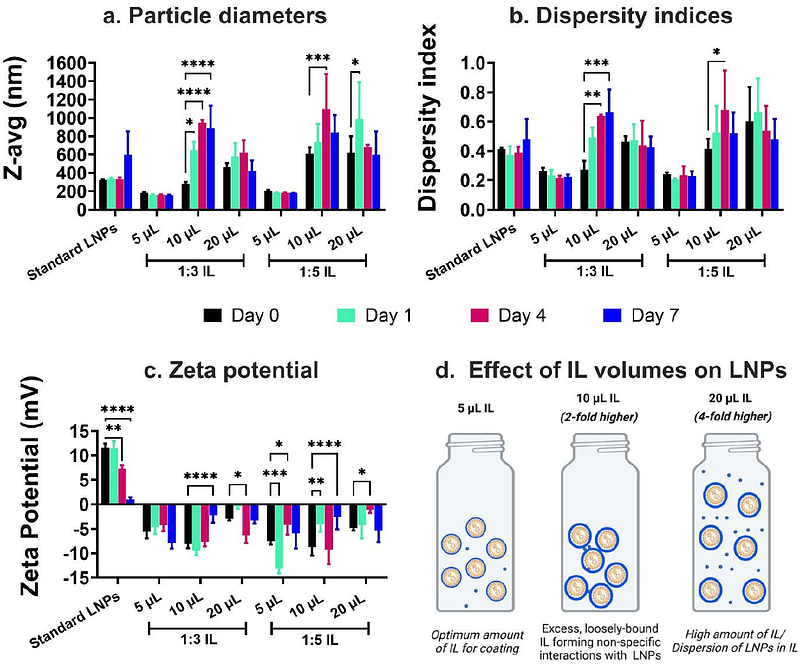
AbstractLipid nanoparticles (LNPs) have transformed the delivery of nucleic acid therapeutics; however, their natural tropism favors the liver resulting in clearance by the reticuloendothelial system, with less than 1% of the injected dose reaching challenging targets such as brain endothelial cells (BECs). Biocompatible ionic liquids (ILs) are tunable materials that can modulate nanoparticle interactions with blood components. Choline trans-2-hexenoate (C2HA) is an IL known to facilitate red blood cell (RBC) hitchhiking of PLGA polymeric nanoparticles and reduces hepatic uptake and therefore enabling transport to distant organs. We wanted to determine if C2HA coatings can show similar RBC hitchhiking effects with LNPs. We previously coated LNPs with ILs to alter their surface properties and reduce serum protein binding to IL-coated LNPs: a key contributor to rapid clearance via the liver. While LNPs coated with choline trans-2-hexenoate at 1:1 and 1:2 cation: anion ratios decreased mouse serum protein binding and improved cellular uptake into brain endothelial cells and motor neurons, they did not show hitchhiking behavior. To identify IL formulations capable of this behavior, we screened higher IL cation: anion ratios (1:3 and 1:5) for LNP coating and optimized IL volumes that allowed stable particle diameters. The resulting IL-coated LNPs successfully hitchhiked on both mouse and human RBCs and significantly enhanced uptake in b.End3 mouse BECs, and NSC-34 neuroblastoma cells compared to uncoated LNPs. 1:3 IL-coated LNPs demonstrated the most pronounced improvement in RBC binding. These findings reveal that ILs can be leveraged to re-engineer clinically approved LNP platforms to promote RBC hitchhiking behavior and further be developed for drug delivery to extra-hepatic targets.