A Dual-Readout Photonic Sensor for Simultaneous Measure-ment of Enzyme Activity and Concentration
A Dual-Readout Photonic Sensor for Simultaneous Measure-ment of Enzyme Activity and Concentration
Butt, J. N.; Steiner, D. J.; Bryan, M. R.; Mann, K. E.; Miller, B.
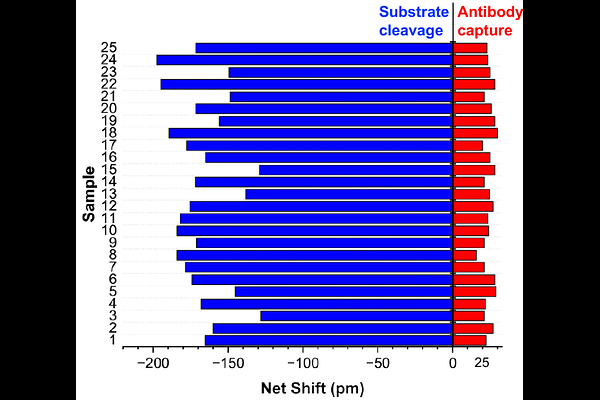
AbstractEnzyme assays are a cornerstone of basic biology and clinical diagnosis. Typically, enzyme activity is meas-ured, but concentration of the enzyme is also of interest, as are comparisons between concentration and activity. In these sit-uations, separate concentration (i.e. ELISA) and activity (i.e. absorbance) assays are required to fully quantify. Here, we re-port a multiplex disposable photonic biosensor for simultaneous measurement of enzyme activity and concentration. Capture of the enzyme by a ring resonator-bound antibody produces a red shift in resonance, which can be referenced to a nonspecific binding control. At the same time, enzyme-mediated degradation of a ring-bound substrate produces a resonance blue shift, which can be referenced to a peptide inert to enzymatic cleavage. We tested the dual assay with human Cathepsin-L, dysfunc-tion of which is a hallmark of several diseases, including COVID-19, kidney failure, and cancer. Both assays were found to be well-behaved analytically, with lower limits of detection of 2.0 ng mL-1 (concentration) and 1.8 ng mL-1 (activity), well within the range clinically relevant concentrations. Further assessment with a panel of 25 single-donor human serum samples confirmed utility of the assay in a complex, biologically relevant matrix. This approach therefore serves as a useful method for Cathepsin-L detection, and a prototype for other dual-mode photonic enzyme assays.