Doxycycline Release From Cyclodextrin Oligomer-Containing Collagen Gels
Doxycycline Release From Cyclodextrin Oligomer-Containing Collagen Gels
Trout, E.; Palomo, L.; von Recum, H. A.; Eppell, S. J.
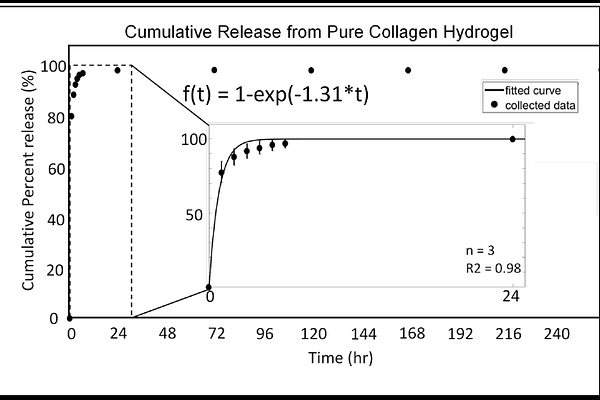
AbstractDental implants commonly suffer from chronic peri-implantitis arising from infection and inflammation at the abutment/gingiva interface, primarily because they fail to replicate the collagen-rich soft tissue interface between natural teeth and the jawbone. Current treatment strategies involve frequent administration of systemic antibiotics and collagenase inhibitors which complicates clinical management. A localized controlled drug-release approach may offer a way to simplify this clinical management. In this study, we investigate doxycycline loading and release from a collagen hydrogel containing entrapped oligomers of gamma-cyclodextrin (CD). Incorporating these cyclodextrin oligomers increased the releasable amount of doxycycline by 220% and reduced its release rate fivefold. The resulting enhancement in both drug loading and release control expands the potential for further development of a collagen-coated dental implant.