Reconfiguration of the visual code and retinal cell type complement in closely related diurnal and nocturnal mice
Reconfiguration of the visual code and retinal cell type complement in closely related diurnal and nocturnal mice
Allen, A. E.; Hahn, J.; Richarson, R.; Pantiru, A.; Mouland, J.; Bano-Otalora, B.; Monavarfeshani, A.; Yan, W.; Williams, C.; Wynne, J.; Rodgers, J.; Milosavljevic, N.; Orlowska-Feuer, P.; Storchi, R.; Sanes, J. R.; Shekhar, K.; Lucas, R. J.
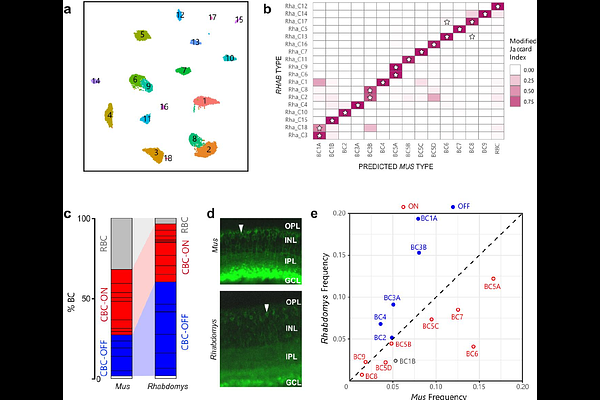
AbstractHow does evolution act on neuronal populations to match computational characteristics to functional demands? We address this problem by comparing visual code and retinal cell composition in closely related murid species with different behaviours. Rhabdomys pumilio are diurnal and have substantially thicker inner retina and larger visual thalamus than nocturnal Mus musculus. High-density electrophysiological recordings of visual response features in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (dLGN) reveals that Rhabdomys attains higher spatiotemporal acuity both by denser coverage of the visual scene and a selective expansion of elements of the code characterised by non-linear spatiotemporal summation. Comparative analysis of single cell transcriptomic cell atlases reveals that realignment of the visual code is associated with increased relative abundance of bipolar and ganglion cell types supporting OFF and ON-OFF responses. These findings demonstrate how changes in retinal cell complement can reconfigure the coding of visual information to match changes in visual needs.