Towards MR-based interrogation of the hypoxia-driven insulin resistance mechanism: Adipocytes size estimation.
Towards MR-based interrogation of the hypoxia-driven insulin resistance mechanism: Adipocytes size estimation.
Morozov, D.; Prentiss, I.; Yamada, N.; Hakhu, S.; Sukstansky, A.; Beeman, S. C.
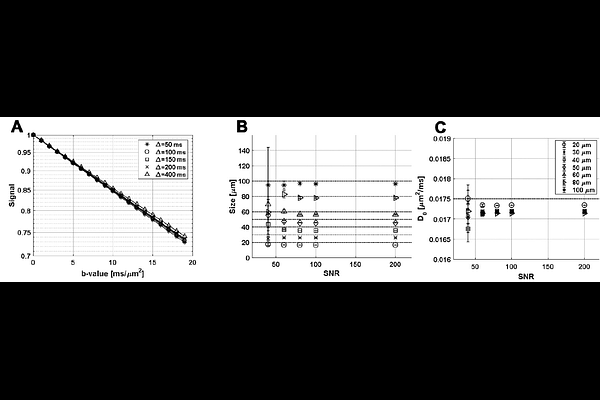
AbstractObesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes, yet not all individuals with obesity develop metabolic disease, underscoring the need for mechanistic biomarkers. Adipocyte hypertrophy is a hypothesized driver of insulin resistance, but current methods for quantifying adipocyte size are invasive. Here, we propose and validate a non-invasive MRI approach based on short diffusion time diffusion-weighted MR spectroscopy to estimate adipocyte size in vivo. Monte Carlo simulations confirmed the method\'s accuracy across a physiologic range of adipocyte sizes (20 - 150 m) and signal-to-noise ratios (SNR > 40). We applied this technique to the epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT) of rats using in vivo 4.7T and ex vivo 11.7T MRI. Adipocyte sizes derived from diffusion MRI showed good agreement with histology, with minor systematic underestimation corrected by empirical factors. This approach does not require complex modeling or high diffusion weighting, increasing its translatability to the laboratory and clinical settings. Diffusion MRI may serve as a non-invasive virtual biopsy to monitor adipocyte morphology and improve understanding of obesity-related metabolic dysfunction.