Immunoinformatic Designing and Evaluation of a Broad-Spectrum Multiepitope Vaccine Against MDR Acinetobacter baumannii, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Immunoinformatic Designing and Evaluation of a Broad-Spectrum Multiepitope Vaccine Against MDR Acinetobacter baumannii, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Bhardwaj, N.; Sah, S. N.; Billa, A.; Gupta, V.; Capalash, N.; Sharma, P.
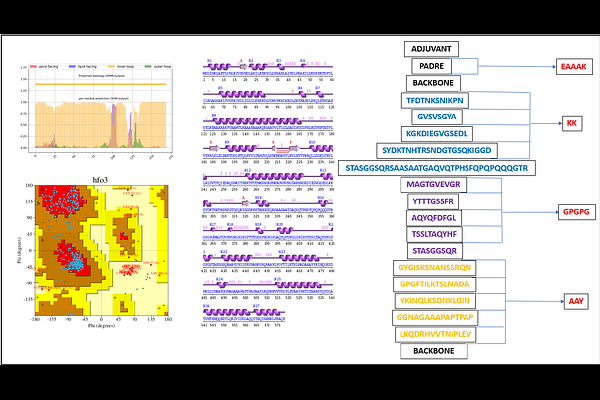
AbstractAcinetobacter baumannii, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa are among the multidrug-resistant (MDR) Gram-negative pathogens that pose a growing threat, necessitating novel preventive measures in addition to traditional antibiotics. By using advanced immunoinformatics methods, highly conserved and immunogenic epitopes for B-cells and T-cells were selected from major virulence-associated proteins (LptE, YiaD, MrkD, PhoE, OprF, and Zot), which exhibited high antigenicity (VaxiJen scores 0.74-2.75) and 98.87% global population coverage. The construct vaccine comprises 50S ribosomal protein L7/L12 adjuvant and PADRE sequence for immunogenicity enhancement, with structural validation indicating stability (96.3% residues in the total allowed Ramachandran regions). High-affinity interactions with TLR2/TLR4 (binding energies: -1009.6 to -1079.6 kcal/mol) were found through molecular docking, and immune simulations suggested strong humoral (IgM/IgG) and cellular (IFN-{gamma}/IL-12) responses. Importantly, MEP vaccines can overcome major drawbacks of traditional vaccines by (1) offering cross-strain protection via conserved epitopes, (2) lowering the need for antibiotics through infection prevention, and (3) providing affordable options for healthcare systems affected by MDR infections. These findings demonstrate the MEP construct\'s potential as a preventative measure against nosocomial infections, which may have implications for combating the global AMR epidemic. Further experimental validation is needed to verify its efficacy.