Beyond the ink: cellular and molecular effects of iron-based pigments on macrophages
Beyond the ink: cellular and molecular effects of iron-based pigments on macrophages
Vitipon, M.; Akingbagbohun, E.; Devime, F.; Diemer, H.; Hirschler, A.; Fenel, D.; Ravanel, S.; CARAPITO, C.; Rabilloud, T.
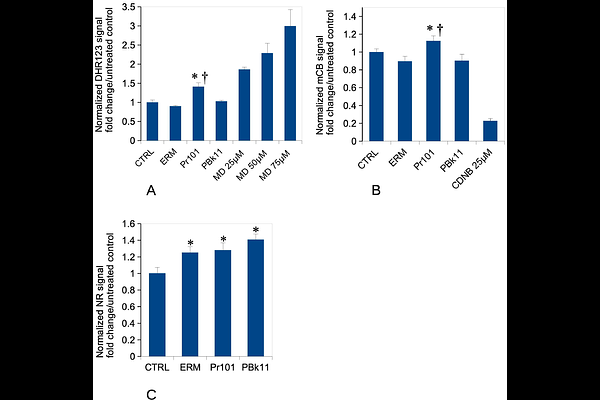
AbstractAs ochre, iron oxide is among the most ancient pigments used by mankind for different purposes, including tattooing as demonstrated on tattoed mummies. Iron oxides are still used in tattooing nowadays and especially in dermopigmentation, an area of medical tattoing aiming at restoring the color of skin. This ancient use of iron oxide does not mean that it has no effect on cells, and especially on macrophages, the cells that maintain pigments particles on site in tattoos. We thus investigated the delayed/sustained effects of iron oxide pigments on macrophages, i.e. the effects occurring a few days after the exposure to pigments, on pigments-loaded macrophages but in a pigment-free medium, mimicking the status of tattooed skin after all the pigment particles have been captured. By combining proteomic and targeted approaches, we determined that red iron oxide (but not black iron oxide) induces perturbations in mitochondria, altering the mitochondrial transmembrane potential. Red iron oxide also induces oxidative stress and the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor. Thus, red iron oxide induces adverse effects on macrophages that may persist over time, owing to its low intracellular dissolution.