Biocompatible Multi-functional Polymeric Material for Mineralized Tissue Adhesion
Biocompatible Multi-functional Polymeric Material for Mineralized Tissue Adhesion
Luo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fulco, S.; Liu, J.; Chen, K.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, R.; Rakesh, L.; Ozer, F.; Tertuliano, O.; Turner, K.; Vining, K. H.
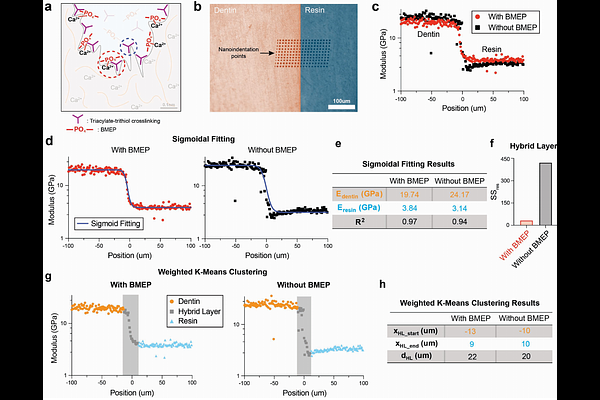
AbstractThis study developed a biocompatible multifunctional thiol-ene resin system for adhesion to dentin mineralized tissue. Adhesive resins maintain the strength and longevity of dental composite restorations through chemophysical bonding to exposed dentin surfaces after cavity preparations. Dental pulp cells are exposed to residual monomers transported through dentinal tubules. Monomers of conventional adhesive systems may result in inhomogeneous polymer networks and the release of residual monomers that cause cytotoxicity. In this study, we develop a one-step multi-functional polymeric resin system by incorporating trimethylolpropane triacrylate (TMPTA) and bis[2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl] phosphate (BMEP) to enhance both mechanical properties and adhesion to dentin. Molecular dynamics simulations identified an optimal triacylate:trithiol ratio of 2.5:1, which was consistent with rheological and mechanical tests that yielded a storage modulus of ~30 MPa with or without BMEP. Shear bond tests demonstrated that the addition of BMEP significantly improved dentin adhesion, achieving a shear bond strength of 10.8 MPa, comparable to the commercial primer Clearfil SE Bond. Nanoindentation modulus mapping characterized the hybrid layer and mechanical gradient of the adhesive resin system. Further, the triacrylate-BMEP resin showed biocompatibility with fibroblasts in vitro. These findings suggest the triacrylate-trithiol crosslinking and chemophysical bonding of BMEP provide enhanced bond strength and biocompatibility for dental applications.