The effects of breastmilk-derived osteopontin on the intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte compartment
The effects of breastmilk-derived osteopontin on the intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte compartment
McClanahan, K. G.; Capella, J.; Gaddy, J.; Olivares-Villagomez, D.
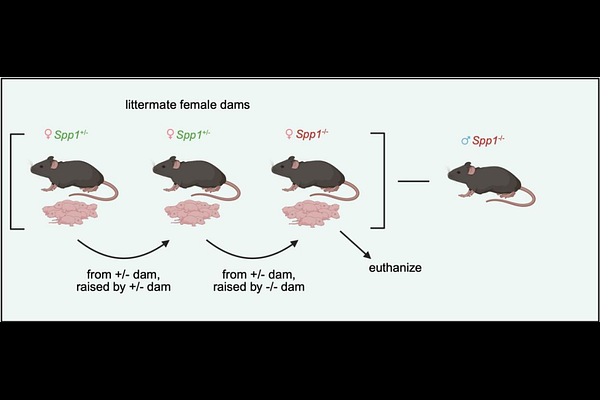
AbstractOsteopontin is a protein with many physiological roles and is widely expressed by many cell types, tissues, and bodily fluids, including breastmilk. The functions of breastmilk osteopontin are not clearly defined, however, it is known to impact intestinal and brain development in infants. Although it is known that endogenous osteopontin influences the survival of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL)2, the impact of breastmilk osteopontin on developing intestinal immune cells remains unclear. In this report, mouse models lacking expression of osteopontin were used to demonstrate that milk-derived osteopontin is important for the development of IELs, with observed effects in both juvenile and adult mice. These changes are most prevalent in IELs expressing CD8: however, the impact of these alterations is unclear, as mice with disrupted IEL compartments are not more susceptible to DSS-induced colitis or infection by Citrobacter rodentium.