Neurocomputational Mechanisms Linking Future Interaction Prospects to Reactive and Proactive Costly Punishment
Neurocomputational Mechanisms Linking Future Interaction Prospects to Reactive and Proactive Costly Punishment
Feng, C.; Huang, C.; Zhou, X.; Liu, F.; Yang, B.; Zheng, Z.; Li, X.; Yin, Y.; Luo, Y.-J.
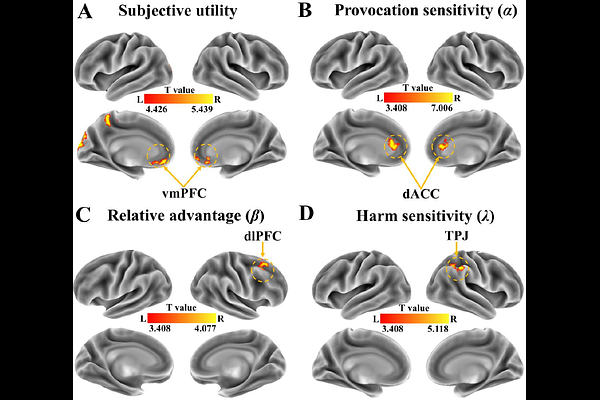
AbstractCostly punishment within social bonds manifests as both reactive penalties for transgressions and proactive sanctions against fair behaviors, yet a unified neurocomputational framework remains elusive. Combining neuroimaging and computational modeling, this study examined how future interaction prospects-a key element of social bonds-modulate reactive and proactive punishment. Participants acted as second- or third-party punishers, responding to allocation offers from individuals with or without future interactions. Results showed that participants imposed harsher punishment on both fair and unfair offers from individuals they did not expect to interact with, aligning with lower self-reported social closeness. Heightened provocation sensitivity, reflected in dorsal anterior cingulate cortex activity, drove the increased reactive punishment toward wrongdoers without future interactions, whereas punishment of future-interacting transgressors was associated with enhanced dorsolateral and dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (dlPFC, dmPFC) activity. A stronger preference for relative advantage and reduced harm sensitivity, linked to dlPFC and temporoparietal junction activity, mediated greater proactive punishment towards non-future-interacting individuals. Moreover, proactive punishment and underlying neurocognitive processes followed a collective retaliation pattern, increasing after unfair (vs. fair) behavior from another non-future-interacting individual. These findings establish a unified neurocomputational framework for understanding how future interaction prospects regulate costly punishment, integrating reactive and proactive motives within social bonds.