Extracting Reproducible Components from Electroencephalographic Responses to Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation with Group Task-Related Component Analysis
Extracting Reproducible Components from Electroencephalographic Responses to Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation with Group Task-Related Component Analysis
Couto, B. A. N.; Fecchio, M. N.; Russo, S.; De Martino, E.; Parmigiani, S.; Sarasso, S.; Graven-Nielsen, T.; de Andrade, D. C.; Massimini, M.; Rosanova, M.; Casali, A. G.
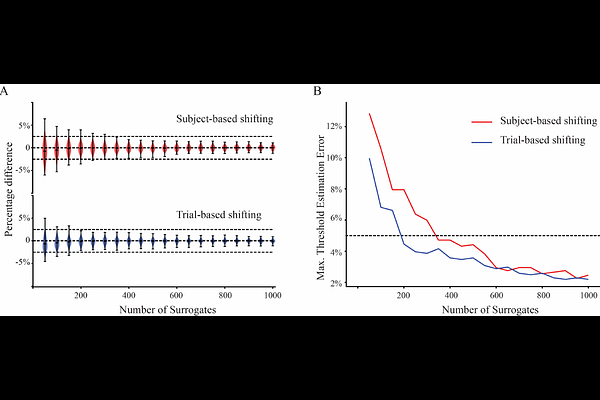
AbstractTranscranial magnetic stimulation combined with electroencephalography (TMS-EEG) is a powerful technique for investigating human cortical circuits. However, characterizing TMS-evoked potentials (TEPs) at the group level typically relies on grand averaging across stimulus repetitions (trials) and subjects - an approach that assumes a level of spatial and temporal consistency that is often lacking in TEPs. Here, we introduce an adaptation of Group Task-Related Component Analysis (gTRCA), a novel multivariate signal decomposition method, to automatically extract TEP components that are maximally reproducible across both trials and subjects. Following the validation of a new permutation-based statistical test for gTRCA using simulated data, the method was applied to two independent TMS-EEG datasets, in which stimulation was targeted to the primary motor cortex (M1) in cohorts of 16 and 22 healthy participants. We found that gTRCA reliably identified TEP components that were reproducible at the group level. Notably, the main gTRCA component captured the key spatial, temporal, and spectral features of motor TEPs, remained robust despite reduced number of stimuli and participants, and was consistent across different recordings. These findings demonstrate that gTRCA affords a more reliable characterization of TEPs at the group level, thereby facilitating the translation of TMS-EEG research into clinical practice.