Influence of Surfactant HLB Values and Agricultural Adjuvants on Pesticide Penetration in Plant Leaves
Influence of Surfactant HLB Values and Agricultural Adjuvants on Pesticide Penetration in Plant Leaves
Bonn, D.
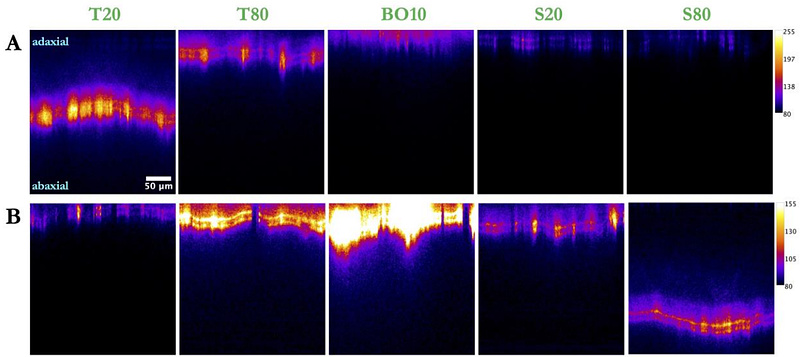
AbstractBACKGROUND: Effective pesticide action is crucial for optimizing efficacy and minimizing environmental impact, particularly with the increasing reliance on systemic pesticides. Surfactants and adjuvants are commonly used to enhance penetration, but their performance depends on the physicochemical properties of both the pesticide and the surfactants used in the formulations. This study examines how surfactant hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) values and commercial adjuvants affect pesticide penetration through plant cuticles. RESULTS: We assessed the penetration of two fluorescent pesticide mimics, Rhodamine B (hydrophilic) and Nile Red (lipophilic), into spring onion leaves using confocal laser scanning microscopy. High HLB surfactants significantly enhanced the uptake of Rhodamine B, while low HLB surfactants promoted Nile Red penetration. Surfactants with intermediate HLB values had minimal effect on either compound. Among seven commercial adjuvants tested, only Squall and Prolong significantly improved the penetration of both mimics. Other adjuvants, despite their common use in agriculture, showed limited or no effect on pesticide uptake. CONCLUSION: The HLB value of surfactants strongly influences pesticide penetration, with optimal uptake achieved when the surfactant HLB aligns with the pesticide polarity. The penetration mechanisms differ: hydrophilic compounds benefit from increased cuticle hydration with high HLB surfactants, while lipophilic compounds penetrate more effectively with low HLB surfactants that enhance wax fluidity. The limited efficacy of most commercial adjuvants suggests that formulation selection should be based on compound-specific properties rather than generalized claims. These findings emphasize the need for targeted adjuvant selection based on the properties of the active ingredient, providing a practical strategy to optimize pesticide formulations for improved efficacy and reduced environmental impacts.