Body Fluid Estimation during Standard Ultrafiltration in Chronic Kidney Disease
Body Fluid Estimation during Standard Ultrafiltration in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abohtyra, R. M.; Beg, O. A.
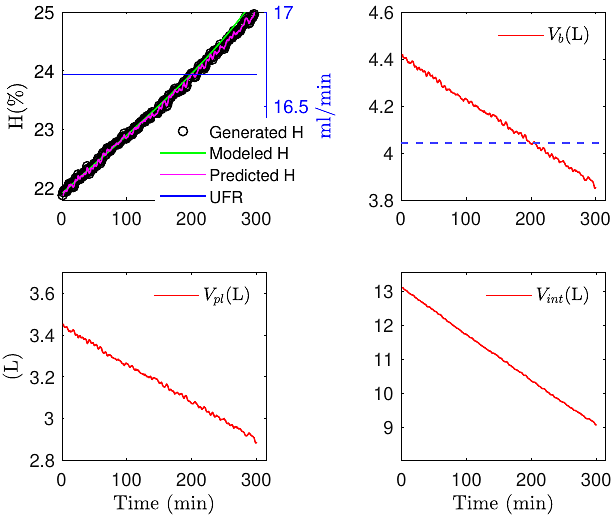
AbstractBackground: Effective management of body fluid volumes and precise ultrafiltration (UF) prescription are critical challenges in treating Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) patients undergoing hemodialysis (HD). Current fluid estimation techniques rely on fluid infusion or restricted UF protocols, which are difficult to implement consistently in daily clinical practice. Objective: This work aims to evaluate whether current blood concentration measurement techniques can identify fluid and absolute blood volumes during regular HD treatments with standard ultrafiltration (UF) profiles (constant rates). Methods: The proposed method is independent of any specific hematocrit sensor, UF rate, or volume infusion protocol. It utilizes modeling and prediction algorithms to quantify errors in fluid volume estimations. Results: The method was tested on model-generated data from two patients under constant UF profiles. Extracellular (plasma and interstitial) fluid and absolute blood volumes were accurately estimated. In one case, specific blood volume dropped from 65 mL/kg to 61 mL/kg, while in the other, it remained above the critical threshold of 65 mL/kg. Conclusion: This estimation algorithm can be easily integrated into existing HD machines, potentially improving treatment outcomes for CKD patients.