Amplification-free Detection of Zoonotic Viruses Using Cas13 and Multiple CRISPR RNAs
Amplification-free Detection of Zoonotic Viruses Using Cas13 and Multiple CRISPR RNAs
Lamb, C.; te Velthuis, A. J. W.; Myhrvold, C.; Nilsson-Payant, B.
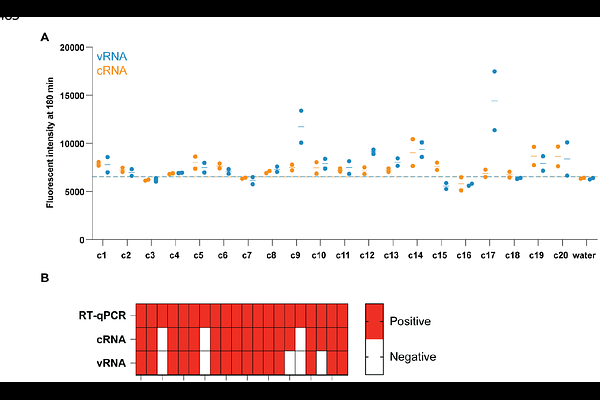
AbstractZoonotic viruses such as hantaviruses and influenza A viruses present a threat to humans and livestock. There is thus a need for methods that are rapid, sensitive, and relatively cheap to detect infections with these pathogens early. Here we use an amplification-free CRISPR-Cas13-based assay, which is simple, cheap and field-deployable, to detect the presence or absence of genomic hantavirus or influenza A virus RNA. In addition, we evaluate whether the use of multiple CRISPR RNAs (crRNAs) can improve the sensitivity of this amplification-free method. We demonstrate that for the hantaviruses Tula Virus (TULV) and Andes Virus (ANDV) a combination of two or three crRNAs provides the best sensitivity for detecting viral RNA, whereas for influenza virus RNA detection, additional crRNAs provide no benefit. We also show that the amplification-free method can be used to detect TULV and ANDV RNA in tissue culture infection samples and influenza A virus RNA in clinical nasopharyngeal swabs. In clinical samples, the Cas13 assay has an 85% agreement with RT-qPCR for identifying a positive sample. Overall, these findings indicate that amplification-free CRISPR-Cas13 detection of viral RNA has potential as a tool for rapidly detecting zoonotic virus infections.