The spectral energy distribution of extreme population A quasars
The spectral energy distribution of extreme population A quasars
Karla Garnica, Deborah Dultzin, Paola Marziani, Swayamtrupta Panda
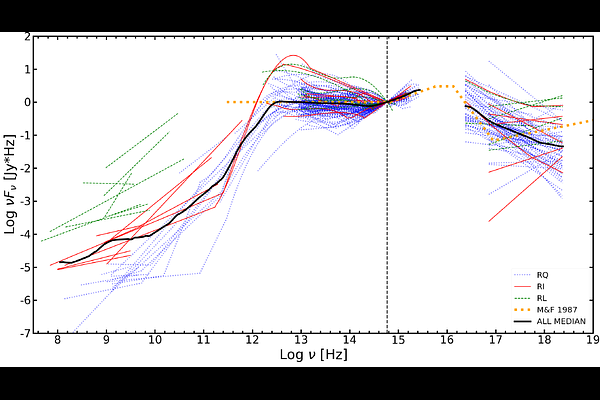
AbstractKnowledge of the broad-band active galactic nuclei (AGN) spectral energy distribution (SED) that ionizes the gas-rich broad emission line region is key to understanding the various radiative processes at play and their importance that eventually leads to the emission line formation. We modeled a spectral energy distribution for highly accreting quasars, also known as extreme population A sources, based mainly on observational data available in astronomical databases, and on accretion disk models for the unobservable far-UV domain. Our selection criterion is the RFeII parameter - the ratio of the optical FeII emission between 4434 A and 4684 A to the H-beta 4861 A intensity, RFeII > 1. This criterion is satisfied by highly-accreting, possibly super-Eddington, black holes. We analyzed 155 sources up to a redshift of approximately 1, previously reported in the literature, to construct a median radio-quiet SED spanning from radio to X-ray wavelengths. We find that the SED of quasars exhibits distinct features compared to lower accreting AGN, including a pronounced big blue bump and strong optical/UV emission along with a steep X-ray continuum. We classify the sources into radio-quiet, radio-intermediate, and radio-loud categories, observing that radio-intermediate and a subsample of radio-quiet AGN show a significant far-IR excess over the radio-quiet SED and the far-IR excess appears to be related to the prominence of Feii emission. There is an overall consistency between the new SED and the one obtained for high Eddington ratio quasars in previous work. We provide the SEDs in digital format for eventual applications.