Live-cell analyses with unsegmented images to study cancer cell response to modified T cell therapy
Live-cell analyses with unsegmented images to study cancer cell response to modified T cell therapy
Epstein, L.; Weiner, A. C.; Verma, A.; Saedi, M.; Carnevale, J.; Marson, A.; Engelhardt, B. E.
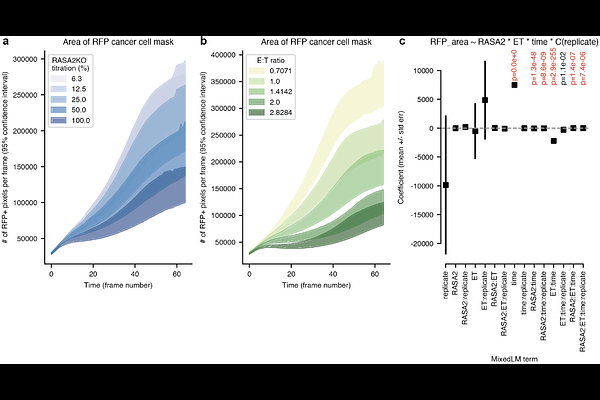
AbstractLive-cell imaging (LCI) of modified T cells co-cultured with cancer cells is commonly used to quantify T cell anti-cancer function. Videos captured by LCI show complex multi-cell behavioral phenotypes that go beyond simple cancer cell fluorescence measurements. Here, we develop an unsupervised analysis workflow to characterize LCI data generated using the Incucyte imaging platform. Unlike most LCI analyses, we avoid cell segmentation due to the low spatiotemporal resolution of the LCI videos and high levels of cell-cell contact. Instead, we develop methods that identify global aggregation patterns and local cellular keypoints to characterize the multicellular interactions that determine cancer cell sensitivity to, or escape from, T cell surveillance. We demonstrate our segmentation-free live-cell behavioral analysis (SF-LCBA) methods on TCR T cells from four donors with varying proportions of cells with a beneficial RASA2 knockout and effector-to-target initial concentrations in a co-culture with A375 melanoma cells. We find that different T cell modifications affect the spatiotemporal dynamics of multicellular aggregate formation. In particular, we show that fewer and smaller cancer cell aggregates form at high ratios of effector T cells to target cancer cells and high titrations of T cells with RASA2 knockouts. Our SF-LCBA method identifies, characterizes, and tracks cellular aggregate formation in datasets that are unsuitable for cell segmentation and tracking, opening the door to more therapeutically-relevant measurements of modified T cell therapy cell behavioral phenotypes from LCI data.