Satellite-assisted Entanglement Distribution with High-Dimensional Photonic Encoding
Satellite-assisted Entanglement Distribution with High-Dimensional Photonic Encoding
V. Domínguez Tubío, M. C. Dijksman, J. Borregaard
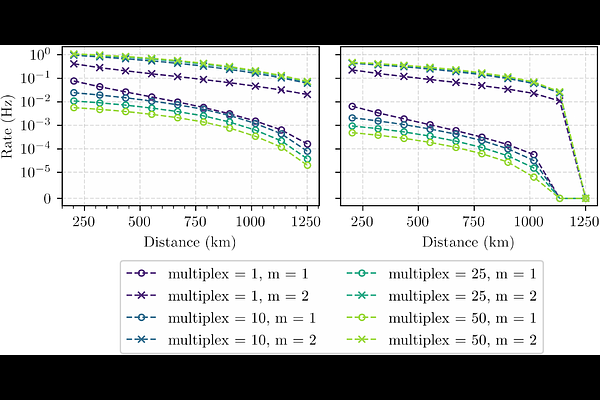
AbstractSatellite-assisted entanglement distribution is a promising approach for realizing long-range quantum networking. However, the limited coherence time of existing quantum memories makes it challenging to obtain multiple event-ready entangled pairs between ground stations since one pair decoheres before the successful distribution of another. We demonstrate how this can be circumvented by pairing existing satellite-compatible spontaneous parametric down conversion (SPDC) sources with qudit-compatible quantum memories on ground. By operating the SPDC source as a source of time-bin encoded photonic qudits, simultaneous distribution of multiple entangled pairs between the ground stations can be achieved at a significantly higher rate than if the SPDC sources was operated as a source of photonic qubits. We find that for achievable coherence times of several seconds and demonstrated satellite performances from the Micius satellite, the qudit operation leads to several orders of magnitude faster distribution rates than the qubit-based operation when more than one event-ready high-quality (Bell pair fidelity $\geq0.95$) entangled pair is desired. To ensure high-quality entanglement distribution, we consider multiplexed quantum memory operation storage and, in the qubit case, we also consider storage cutoff times.