Measurement of Gravitational Time Dilation: An Undergraduate Research Project
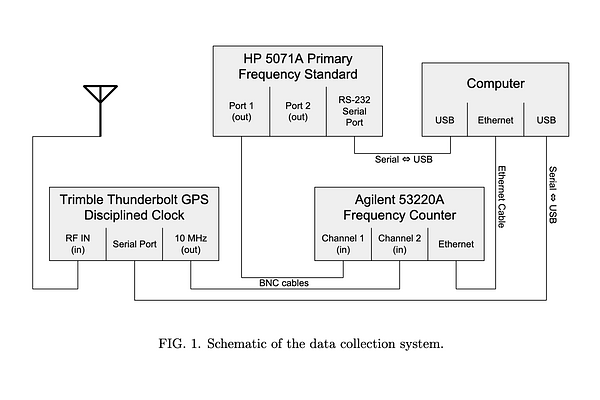
Measurement of Gravitational Time Dilation: An Undergraduate Research Project
M. Shane Burns, Michael D. Leveille, Armand R. Dominguez, Brian B. Gebhard, Samuel E. Huestis, Jeffery Steele, Brian Patterson, Jerry F. Sell, Mario Serna, M. Alina Gearba, Robert Olesen, Patrick O'Shea, Jonathan Schiller
AbstractGeneral relativity predicts that clocks run more slowly near massive objects. The effect is small---a clock at sea level lags behind one 1000 m above sea level by only 9.4 ns/day. Here, we demonstrate that a measurement of this effect can be done by undergraduate students. Our paper describes an experiment conducted by undergraduate researchers at Colorado College and the United States Air Force Academy to measure gravitational time dilation. The measurement was done by comparing the signals generated by a GPS frequency standard (sea-level time) to a Cs-beam frequency standard at seven different altitudes above sea level. We found that our measurements are consistent with the predictions of general relativity.