RNA binding regulation is a new dimension in the type I IFN response
RNA binding regulation is a new dimension in the type I IFN response
Iselin, L.; Demyanenko, Y.; Palmalux, N.; Embarc Buh, A.; Kamel, W.; Simmonds, P.; Mohammed, S.; Castello, A.
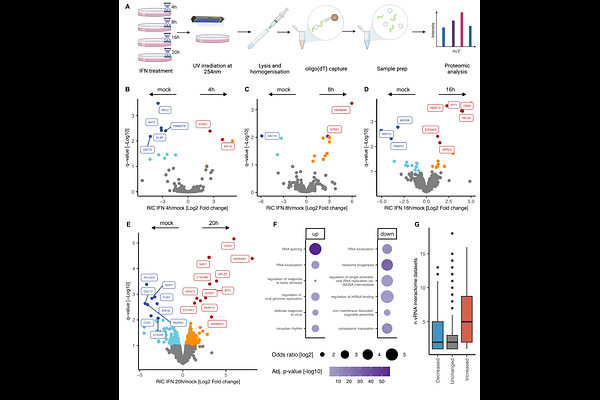
AbstractThe type I interferon (IFN-I) response shapes the intracellular environment to supress virus infection. Historically, this remodelling has been linked to the transcriptional induction of interferon stimulated genes (ISGs). However, IFN-I-driven post-translational regulation of proteins already present in the cell remains relatively unexplored. Here, we profiled the activity of cellular RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), which are key players in antiviral immunity. Using RNA interactome capture (RIC), we identified hundreds of RBPs whose association with RNA is regulated by IFN-I (IR-RBPs). Among these IR-RBPs are both known antiviral proteins and novel candidates identified in this study through a knockdown screen. By modifying RIC to study IR-RBPs\' phosphorylation states, we identified several putative instances of IFN-I-driven phospho-regulation of RNA binding. We experimentally confirmed this phospho-driven regulation for MATR3. Altogether, our results reveal a new dimension of the cell\'s antiviral programme, in which the cellular RNA-bound proteome is remodelled by IFN-I.