Distinguishing Specific from Broad Genetic Associations between External Correlates and Common Factors
Distinguishing Specific from Broad Genetic Associations between External Correlates and Common Factors
de la Fuente, J.; Londono-Correa, D.; Tucker-Drob, E. M.
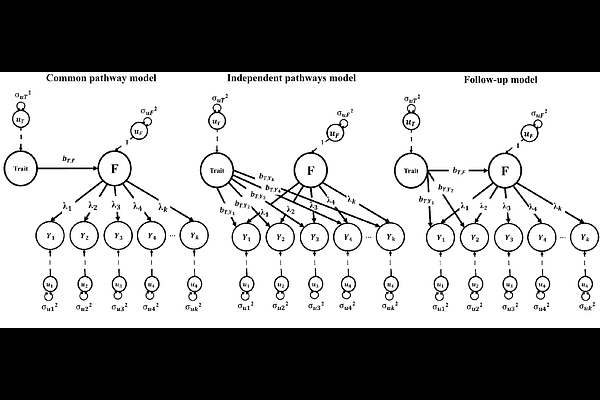
AbstractWithin the Genomic SEM framework, common factors are often used to index shared genetic etiology across constellations of GWAS phenotypes. A standard common pathway model, in which a genetic association is estimated between an external GWAS phenotype and a common factor, assumes that all genetic associations between the external GWAS phenotype and the individual indicator phenotypes are mediated through the factor. This assumption can be tested using the QTrait statistic, which compares the common pathway model to an independent pathways model that allows for direct genetic associations between the external GWAS phenotype and the individual indicators of the factor. We expand upon the QTrait approach by describing an effect size index that quantifies the degree to which the common pathways model is violated, and we provide a systematic approach for empirically identifying specific direct pathways between an external trait and indicator traits. Our method comprises a series of omnibus tests and outlier detection algorithms indexing the heterogeneity of associations between the genetic component of external traits and the individual indicators of common factors. We provide a set of automated functions which we apply to investigate the patterns of genetic associations across a set of external correlates with respect to indicators of general cognitive ability and case-control and proxy GWAS indices of Alzheimer's disease.