Hsp90-dependent triage of the glucocorticoid receptor via the CHIP E3 ubiquitin ligase
Hsp90-dependent triage of the glucocorticoid receptor via the CHIP E3 ubiquitin ligase
Chio, C. M.; Noddings, C. M.; Wang, F.; Agard, D. A.
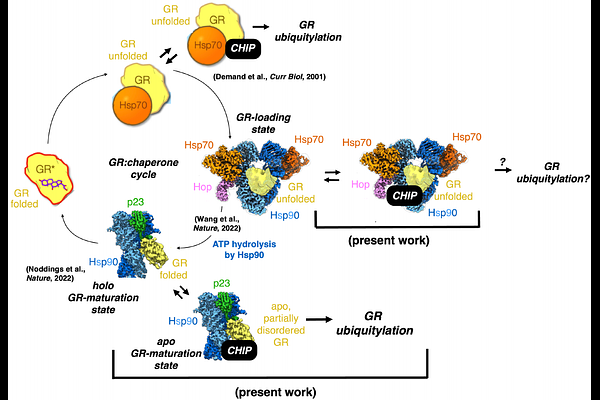
AbstractThe molecular chaperone Hsp90 is required to ensure the proper folding and activation of approximately 10% of the proteome throughout their cellular lifetime1,2. Given that Hsp90 recognizes and preferentially interacts with partially unfolded client states, it is well-poised to promote the degradation of misfolded clients and clients past the point of re-foldability3,4,5. Long-standing phenomenological data suggest that Hsp90 could directly present a client protein to an E3 ubiquitin ligase, in this way mediating degradative ubiquitylation of the client. However, this has yet to be directly demonstrated for any client. To assess this mechanism for the model Hsp90 client the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), a ligand-dependent transcription factor, we reconstituted in vitro the Hsp90-dependent folding cycle for GR6, in the presence of the E3 ligase CHIP. Remarkably, we discovered that CHIP binds to and efficiently ubiquitylates GR as presented by a previously characterized Hsp90-dependent pro-folding state called the GR-maturation state (Hsp90-p23-GR), in which GR has been visualized via cryo-EM to be folded in the native state and ligand-bound7. We determined a low-resolution (~14 [A]) cryo-EM reconstruction of the four-component Hsp90-p23-GR-CHIP complex, and furthermore resolved from the same dataset a 3.53 [A] reconstruction of a Hsp90-p23-GR complex in which, surprisingly, GR is partially disordered and ligand-free--in contrast with what we previously observed7, presumably as a consequence of interaction with CHIP. Our results suggest a mechanism by which Hsp90 can simultaneously partition a client between both folding and degradation outcomes and in this way directly mediate protein-triage decisions through its interactions with E3 ligases.