Membrane remodeling by the Bacterial Dynamin-like Protein (BDLP) from Nostoc punctiforme
Membrane remodeling by the Bacterial Dynamin-like Protein (BDLP) from Nostoc punctiforme
Singh, K.; Pucadyil, T.
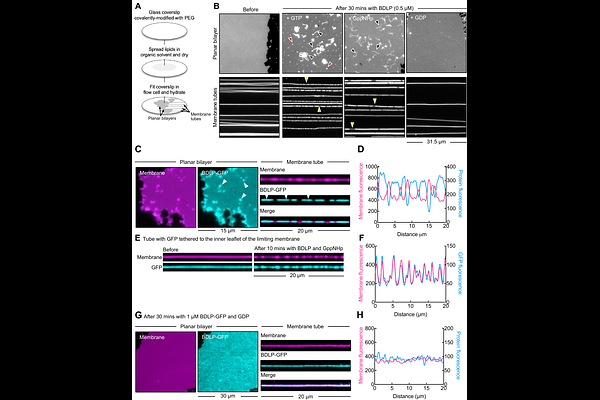
AbstractMembranes are fundamental to biological systems as they serve as barriers to compartmentalize the cell and its cytoplasm. They are constantly remodeled in shape and composition during the formation and maintenance of organelles. The large GTPase dynamins are well characterized for membrane shape remodeling in eukaryotes but their functions in prokaryotes are less characterized. Here, we determine the lipid-binding, enzymatic and membrane remodeling activities of the Bacterial Dynamin-Like Protein (BDLP) from the cyanobacterium Nostoc punctiforme. We find that BDLP binds phosphatidylglycerol (PG)-containing membranes, but unlike other soluble dynamins, shows little stimulation in GTPase activity. This enzymatic feature is like that seen among the fusion dynamins to which BDLP shows structural similarities. FRET-based bulk vesicle fusion assays however reveal that BDLP is incapable of membrane fusion. To further understand BDLP functions, we turned to microscopic analysis of BDLP on membranes templates. We find that the GTP-bound BDLP forms a rigid scaffold that is capable of bending and imposing a defined curvature. In contrast, the GDP-bound state is loosely organized and unable to remodel membrane shape. Our results indicate that BDLP intrinsically functions as a protein scaffold whose organization is regulated by nucleotide binding.