KOLF2.1J iTF-Microglia: A standardized platform to studymicroglial transcriptional regulatory networks in CNS disease
KOLF2.1J iTF-Microglia: A standardized platform to studymicroglial transcriptional regulatory networks in CNS disease
Rodriguez-Nunez, I.; Bartley, S. C.; Taylor, J. W.; Johnston, S. Q.; Rogers, B. B.; Meadows, S. K.; Newberry, K. M.; Cochran, J. N.; Myers, R. M.
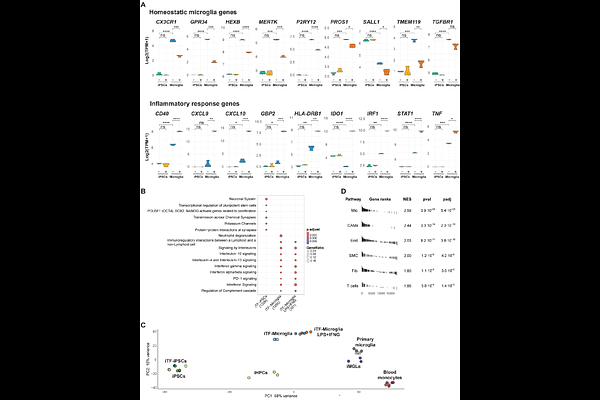
AbstractUnderstanding transcriptional regulatory networks (TRNs) in microglia is key to uncovering mechanisms driving central nervous system (CNS) disorders. Human iPSC-derived models offer a tractable system for studying microglia, yet variability between lines has limited reproducibility. Here, we use the standardized KOLF2.1J iTF line to rapidly generate microglia-like cells (iTF-Microglia) and profile TRNs under homeostatic and inflammatory conditions. iTF-Microglia closely resemble primary brain microglia at both transcriptomic and epigenomic levels. Integrative analyses reveal microglia-enriched candidate cis-regulatory elements (cCREs) and dynamic enhancer remodeling upon differentiation and LPS+IFNG stimulation, involving key transcription factors (TFs) including NF-kB, IRF, and STAT families. TRNs active in iTF-Microglia are enriched for genetic variants linked to Alzheimer\'s disease and other CNS disorders. These findings establish KOLF2.1J iTF-Microglia as a reproducible and genetically tractable platform for studying human microglial gene regulation and provide mechanistic insight into how TRN remodeling may contribute to CNS disease risk.