Comparative analysis of genomic prediction approaches for multiple time-resolved traits in maize
Comparative analysis of genomic prediction approaches for multiple time-resolved traits in maize
Hobby, D.; Lindner, R.; Mbebi, A. J.; Tong, H.; Nikoloski, Z.
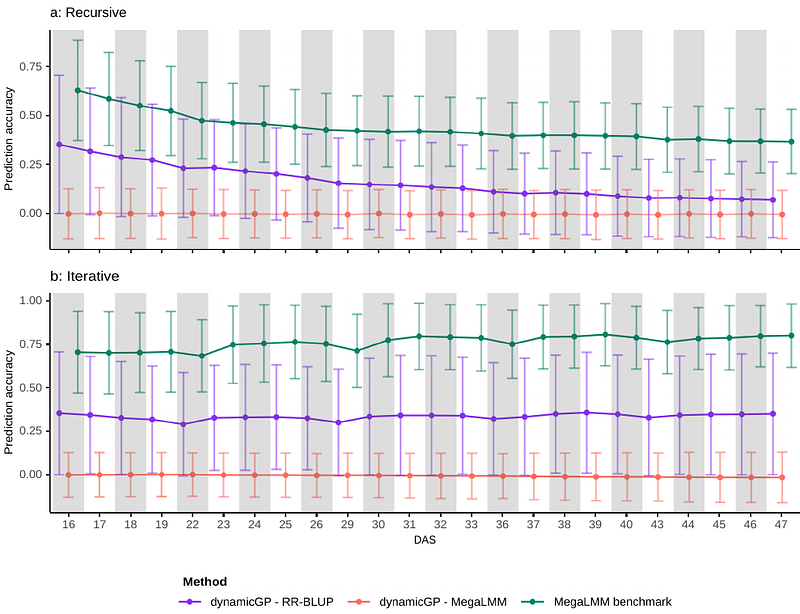
AbstractAbility to accurately predict multiple growth-related traits over plant developmental trajectories has the potential to revolutionize crop breeding and precision agriculture. Despite increased availability of time-resolved data for multiple traits from high-throughput phenotyping platforms of model plants and crops, genomic prediction is largely applied to a small number of traits, often neglecting their dynamics. Here, we compared and contrasted the performance of MegaLMM and dynamicGP as well as their hybrid variants that can handle high-dimensional temporal data for multi-trait genomic prediction. The comparative analysis made use of time series for 50 geometric, colour, and texture traits in a maize multi-parent advanced generation inter-cross (MAGIC) population. The performance of the approaches was assessed using snapshot accuracy and longitudinal accuracy, We found that MegaLMM outperforms dynamicGP in terms of snapshot accuracy, while dynamicGP proved superior in terms of longitudinal accuracy. This study paves the way for careful investigation of factors that affect the capacity to predict dynamics of multiple traits from genetic markers alone. providing insight into the ability to predict multiple traits at a single time point or the dynamics of individual traits over the considered time domain, respectively.