A possible two-fold scenario for the disc-corona of the luminous AGN 1H 0419--577: a high-density disc or a warm corona
A possible two-fold scenario for the disc-corona of the luminous AGN 1H 0419--577: a high-density disc or a warm corona
Delphine Porquet, James N. Reeves, Valentina Braito
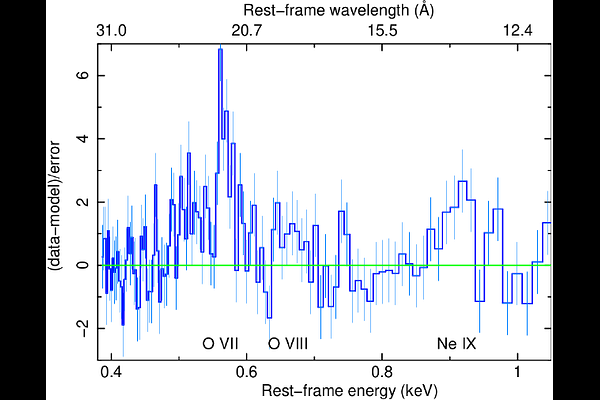
Abstract[abridged] 1H 0419-577 is a highly-accreting, luminous BLS1 AGN. This study aims to characterise its disc-corona system using, for the first time, simultaneous XMM-Newton and NuSTAR observations, performed in May and November 2018. We conducted high-resolution grating spectroscopy to identify potential soft X-ray absorption and emission features. To measure the hot corona temperatures from the spectral analysis above 3 keV, we also included data from a previous NuSTAR observation from June 2015. We characterised the disc-corona system properties by analysing the broadband spectra and the SED from UV to hard X-rays. 1H 0419-577 was observed in a bare-like high-flux state at both epochs, with negligible neutral and ionised absorption along its line of sight at both Galactic and AGN rest-frames. However, several soft X-ray emission lines were detected, notably a broad and intense OVII line indicating an accretion disc origin at only a few tens of gravitational radii. The broadband X-ray spectra revealed a prominent, absorption-free smooth soft X-ray excess, a weak Fe Kalpha complex, and a lack of a Compton hump. Fitting data above 3 keV yielded apparent moderate hot corona temperatures of ~20-30 keV for the 2018 and 2015 observations, depending on the model applied. The 2018 X-ray broadband spectra were well reproduced by either a relativistic reflection model with a high-density accretion disc (~10^18 cm^-2), or a hybrid model combining warm and hot coronae with relativistic reflection. We performed the SED analysis for the latter scenario, which indicated that both the hot and warm coronae would have a small spatial extent. Both scenarios can successfully reproduce the two 2018 observations of 1H 0419-577, but they imply very different physical conditions, for example, in terms of disc density, temperature and accretion power released in the hot corona and the origin of the UV emission.