Overcoming treatment resistance mediated by the bone marrow vascular niche in acute myeloid leukemia
Overcoming treatment resistance mediated by the bone marrow vascular niche in acute myeloid leukemia
Froid, M.; Branciamore, S.; Chen, Z.; Frankhouser, D.; Fu, Y.-H.; Ambriz, J. R.; Nguyen, L. X. T.; Irizarry, J.; Kuo, Y.-H.; O'Meally, D.; Zhang, B.; Marcucci, G.; Rockne, R.; Basanta, D.
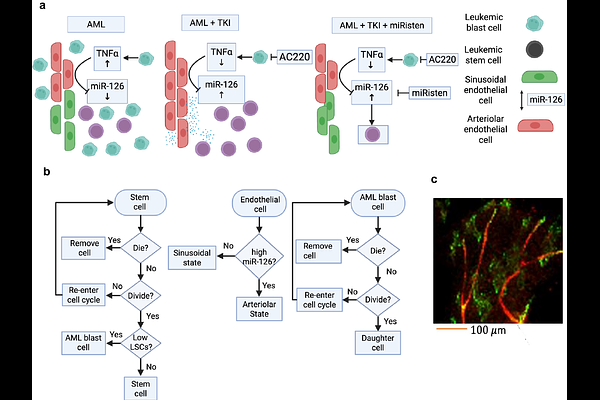
AbstractAcute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a hematologic malignancy originating in the bone marrow, frequently progressing to extramedullary sites. Despite advances in molecularly targeted therapies and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, clinical outcomes remain suboptimal. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) confer benefit in a subset of AML patients harboring FLT3-ITD mutations, yet relapse and resistance are common. These failures are driven by both intrinsic properties of leukemic stem cells (LSCs) - a quiescent, self-renewing population - and extrinsic cues from the tumor microenvironment. We previously demonstrated that arteriolar endothelial cells (ECs) produce miR-126, which is transferred to LSCs, promoting quiescence, treatment resistance, and niche retention. During disease progression, TNF secreted by expanding blasts suppresses EC miR-126 production, enabling LSCs and their progeny to proliferate. Following TKI administration, blast reduction lowers TNF levels, restoring EC miR-126 production and enabling LSCs to re-enter quiescence - thereby escaping therapy and facilitating relapse. To investigate this dynamic, we developed an agent-based computational model of the AML bone marrow microenvironment, parameterized with in vitro and in vivo data. The model captures vascular niche remodeling and the feedback between leukemic populations and endothelial signaling. Simulations reveal that LSC protection mediated by miR-126 can be overcome by combining TKIs with miRisten, a miR-126 inhibitor. When administered on a defined schedule, this combination disrupts the protective niche and enhances LSC eradication. These findings underscore the therapeutic potential of targeting microenvironmental feedback to overcome resistance and prevent AML relapse.