Reproducibility and Accuracy of Nanopore-Based Methylome Profiling of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis Strains from Cancer Patients
Reproducibility and Accuracy of Nanopore-Based Methylome Profiling of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis Strains from Cancer Patients
Schababerle, T.; Hayat, O.; Jung, J.; Le, M.; Polic, I.; Wees, H.; Bhatti, M.; Shelburne, S.; Liu, X.; Kalia, A.
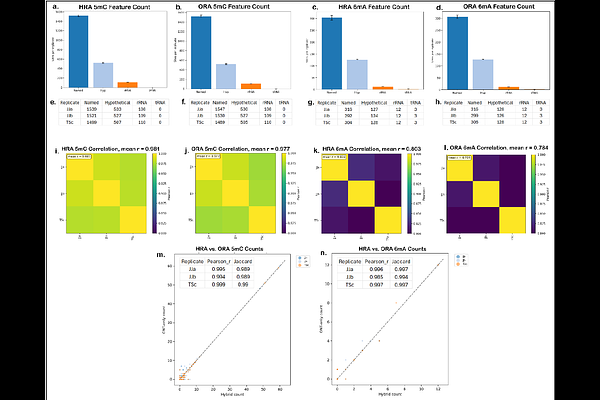
AbstractBackground: DNA methylation influences bacterial gene regulation, virulence, and restriction-modification (RM) systems. Advances by Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) now enable direct methylome profiling from nanopore sequencing using the Dorado basecaller. However, the comparative performance of ONT-only versus hybrid-assembly reference-based methylation calling, particularly regarding genomic DNA quality and inter-operator variability, remains understudied. Methods: Six operators independently prepared fifteen sequencing libraries each for nanopore (MinION R10.4.1 flow cells, Mk1D) and Illumina MiniSeq platforms for two Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis strains (UT9728, 12 replicates; UT10237, 3 replicates). MicrobeMod v1.0.3 was used to identify methylation and motif profiles using Illumina-corrected hybrid reference assemblies (HRAs) and ONT-only reference assemblies (ORAs). Reproducibility and accuracy were compared using a custom genome annotation feature-enabled modular analysis that mapped and counted methylation site calls to CDS, rRNA and tRNA coordinates. Results: Strain UT9728 predominantly exhibited N6-methyladenine (6mA) at GATC motifs, whereas strain UT10237 displayed dual methylation patterns: C5-methylcytosine (5mC) at CCWGG motifs and 6mA at GAGNNNNNTAA motifs. Both strains contained Type I and Type II RM systems; UT10237 uniquely harbored a Type IIG RM system with combined restriction and methylation activities. Motif identification concordance using HRAs and ORAs exceeded 99.9%. Reproducibility for methylation calls was high across independent replicates for both HRA (Pearson\'s r >0.989) and ORA (Pearson\'s r >0.993) methylation calls in GATC and CCWGG motifs but lower in the GAGNNNNNTAA motif (Pearson\'s r (HRA) = 0.80; r (ORA) = 0.78). ORA-based methylation site calls for all motifs showed excellent precision and recall compared to HRA-based calls (F1-score >99.999%). Conclusion: Our findings support the accuracy, robustness, and utility of ONT-only data based methylome profiling for bacterial epigenetic characterization. Our analytical framework facilitates detailed evaluations of reproducibility and accuracy.