Control of myogenesis by the E3 ubiquitin ligase CUL3-BTBD9
Control of myogenesis by the E3 ubiquitin ligase CUL3-BTBD9
Padovani, C.; Perez, F. R.; Tsai, M.; Xiong, J.; Pogson, A.; Martinez, B.; Rape, M.
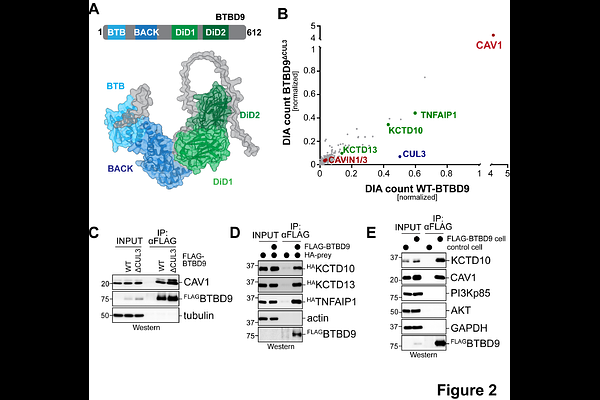
AbstractMetazoan development requires that cells adopt specific identities at the right time and place with-in an embryo. Central to the success of this process are posttranslational modifications that con-trol the activity, stability or localization of crucial transducers of differentiation signals. During muscle development, modification of proteins with ubiquitin is known to play an important role, but the enzymatic machinery of ubiquitylation that drives myogenesis remains incompletely under-stood. Here, we identify CUL3BTBD9 as an E3 ubiquitin ligase that is essential for myogenesis in vitro. CUL3BTBD9 binds and ubiquitylates CAV1, the central component of caveolae that modulate insulin signaling during muscle formation. CUL3BTBD9 and CAV1 are required for insulin-dependent activation of the AKT kinase in myoblasts, thereby safeguarding the ability of muscle precursors to respond to insulin signals. Together, this work identifies CUL3BTBD9 as a regulator of myogenesis that acts by modulating plasma-membrane localized events critical for cell fate specification.