Evaluating the antiviral activity of Termin-8 and Finio against a surrogate ASFV-like algal virus
Evaluating the antiviral activity of Termin-8 and Finio against a surrogate ASFV-like algal virus
Palowski, A.; Domingues, F.; Lopez, O.; Holcombe, N.; Shurson, G.; Schroeder, D.
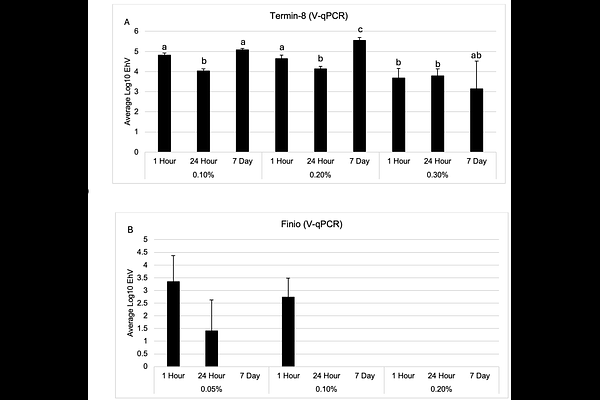
AbstractIntroduction: Anitox has developed and markets Termin-8 (a formaldehyde-based product) and Finio (non-formaldehyde solution) for the control microbial contamination in feed. To date, both Finio and Termin-8 have not been tested for their potential antiviral activity against megaviruses, such African swine fever virus (ASFV) and its surrogate algal virus, Emiliania huxleyi virus (EhV). Given the limited access and great expense for routine chemical mitigation testing with ASFV, we focused on using EhV as a safe and effective surrogate to evaluate the antiviral activity of these Anitox products. The specific objective of the current study was to evaluate the time course of incubation from hours to days to mimic possible field relevant exposure times for the potential preventative mitigation of megaviruses using Termin-8 and Finio. Methods: Emiliania huxleyi virus was treated with the Anitox recommended concentrations of Termin-8 (0.1% to 0.3% final) and Finio (0.05% to 0.2% final) in biological triplicate experiments. Both viability qPCR (V-qPCR) and standard PCR (S-qPCR) were conducted for EhV copies at 1 hr, 5 hrs, 24 hrs and day 7 post-inoculation. Results: We observed that both Termin-8 and Finio, at their highest treatment concentrations, showed the greatest log reduction of 2 and 4.5 log10 units, respectively, at the earliest 1 hr post-inoculation time point. Although Termin-8 efficacy did not improve with time, treatment with Finio showed 100% viable viral inactivation (>5 log10 reduction units) at the lowest concentration after 7 days of exposure. In addition, Finio showed negligible viral DNA removal post-treatment as observed via S-qPCR, but use of Termin-8 resulted in a reduction of viral DNA (S-qPCR) equivalent to that observed using the V-qPCR assay. Discussion: Our results demonstrate for the first time that both Termin-8 and Finio can be used as effective chemical mitigants against megaviruses such as EhV and ASFV. Moreover, the mechanism of chemical mitigation involves degradation of the virus particle itself. However, although Termin-8 efficacy appeared to be less than that of Finio, this is likely not the case because Termin-8 cross-links protein viral capsids and fixes the viral particle to make it non-infectious. With the threat of ASFV introduction into the North American swine industry and other non-infected regions around the world, the use of both Termin-8 and Finio as an effective preventive or mitigation strategy to prevent the transmission of ASFV by reducing particle viability in contaminated feed. Additional research is warranted with ASFV, in the presence of various types of feed ingredients and complete feeds and use bioassays to evaluate infectivity because results from V-qPCR revealed that intact viable particles remain post-treatment.