IL-17A potentiates malignant T-cell viability via electron transport chain complex I in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
IL-17A potentiates malignant T-cell viability via electron transport chain complex I in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
Attrish, D.; Dhamija, B.; Mukherjee, D.; Sawant, V.; Marathe, S.; Saul, D.; Basu, M.; Banik, A.; Sharma, N.; Shet, T.; Jain, H.; Kosinsky, R. L.; Sharma, P.; Purwar, R.
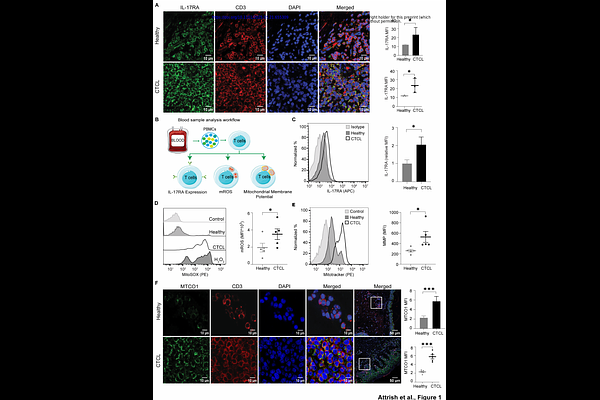
AbstractCutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) is a rare malignancy of skin-resident T cells characterized by an aberrant cytokine profile, notably elevated Interleukin-17A (IL-17A) levels. However, the functional importance of IL-17A dysregulation in the CTCL pathogenesis remains poorly understood. Our analysis revealed increased IL-17A receptor (IL-17RA) expression in CTCL patient samples, supporting the importance of IL-17A signaling in CTCL progression. Proteomic and metabolomic profiling of IL-17A-treated malignant T cells revealed mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC) complex I as a key downstream target of IL-17A signaling. Furthermore, we confirmed the elevated expression of ETC complex I in CTCL patient samples compared to healthy control T cells, hence highlighting the clinical relevance of the IL-17A signaling-ETC complex 1 axis. Altogether, our data unveil the function of IL-17A signaling in the metabolic axis in CTCL progression, which could be useful for developing advanced therapeutic strategies.